Introduction
Data proliferation is transforming businesses. To harness this data for forecasting trends and enhancing efficiencies, AI’s role is pivotal. Yet, AI’s complexity often hampers its corporate adoption. This blog underscores AI observability’s critical role in development. Observability extends beyond monitoring; it’s the granular insight into AI systems—from data acquisition to real-world application. Such transparency is crucial for deploying AI that’s not only effective but also trustworthy.
For example, consider the healthcare sector, where AI models predict patient outcomes. Observability ensures these predictions are accurate and reliable, a non-negotiable in medical applications. Google Health’s research on AI for breast cancer screening highlights observability’s value, showing reduced false positives and negatives.
In practice, observability entails meticulous performance tracking and continuous refinement. This post explores observability’s best practices, equipping you to deploy AI solutions that are both innovative and dependable. Stay tuned for actionable insights that will elevate your AI initiatives to the next level.
What is AI observability?
To achieve optimal performance and desired results, it is essential to comprehend the exact meaning of “observability” in the context of AI applications. The observability feature plays a critical role in ensuring the efficacy and triumphant implementation of the technology. Essentially, observability in AI pertains to the capacity to observe, debug, and comprehend the behavior of ML models in production settings. It enables precise monitoring of model inputs over an extended period, enabling prompt identification of any drifting parameters or anomalies without interfering with the user experience or unnecessarily compromising model performance metrics such as precision and recall scores.

Why is AI Observability Important?
Without proper tracking, an AI solution resembles a car lacking a speedometer or GPS; you cannot tell how well you are performing or where you are going. Now that we know what observability means and what it is about. Let us explore the impact it can create if implemented in AI systems.
The AI system must have below two major properties monitored.
Data Drift
One of the primary challenges is the data distribution shift, which occurs when the data used to train an ML model differs from the data it encounters in production. As a result, the model’s performance may degrade, leading to incorrect or biased predictions. Data drift typically results from seasonal fluctuations or evolving customer preferences. For example, there is a noticeable difference in demand for Face masks in covid and post covid era. Hence, models created using past data are meaningless. The model becomes muddled as a result of the changing input data since the distribution of the variables changes. With observability, data scientists can detect and mitigate data distribution shifts by monitoring and comparing the input data to the training data.
Concept Drift
Concept drift occurs when the underlying relationship between features and the target variable changes over time. This can lead to inaccurate predictions and compromised performance. For example, the season can affect temperature data, even if it’s not explicitly expressed in the data – this is one factor in meteorological data. Similarly, the evolution of consumer spending trends may reflect economic strength without being explicitly stated in the report. We can divide Concept Drift into four categories:
- Sudden Drift
- Gradual Drift
- Incremental Drift
- Recurring Concepts
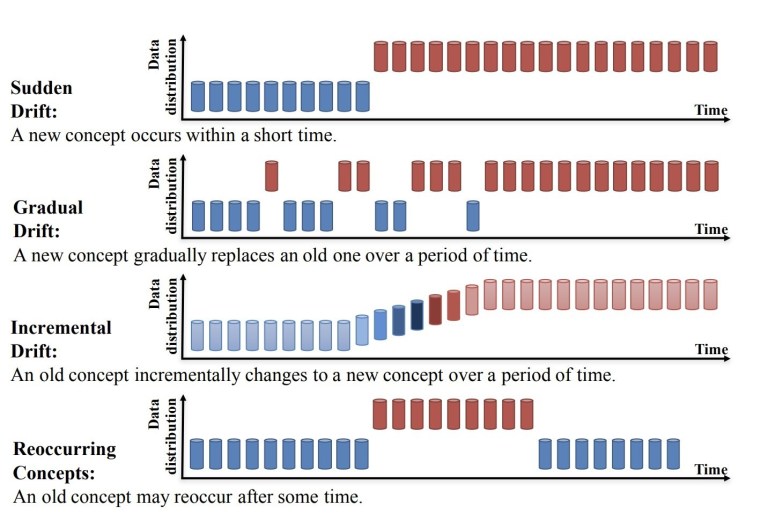
By monitoring the output of Machine Learning models in production over time, you can detect concept drift and enable data scientists to retrain the model or adjust its parameters. With the help of ML Observability, teams can assess and analyze the impact of underlying causes on performance degradation by comparing shifts with baselines from training, validation, or previous production periods.

When issues arise, ML observability gives practitioners the ability to identify the reasons why a model’s performance is not what is anticipated in production. It also provides them with clear signals for when they should retrain their models, update their training datasets, add new features to their models, or even start over. Similar to how data observability helps answer the why, ML observability enables model owners to do root cause analysis of model failures.
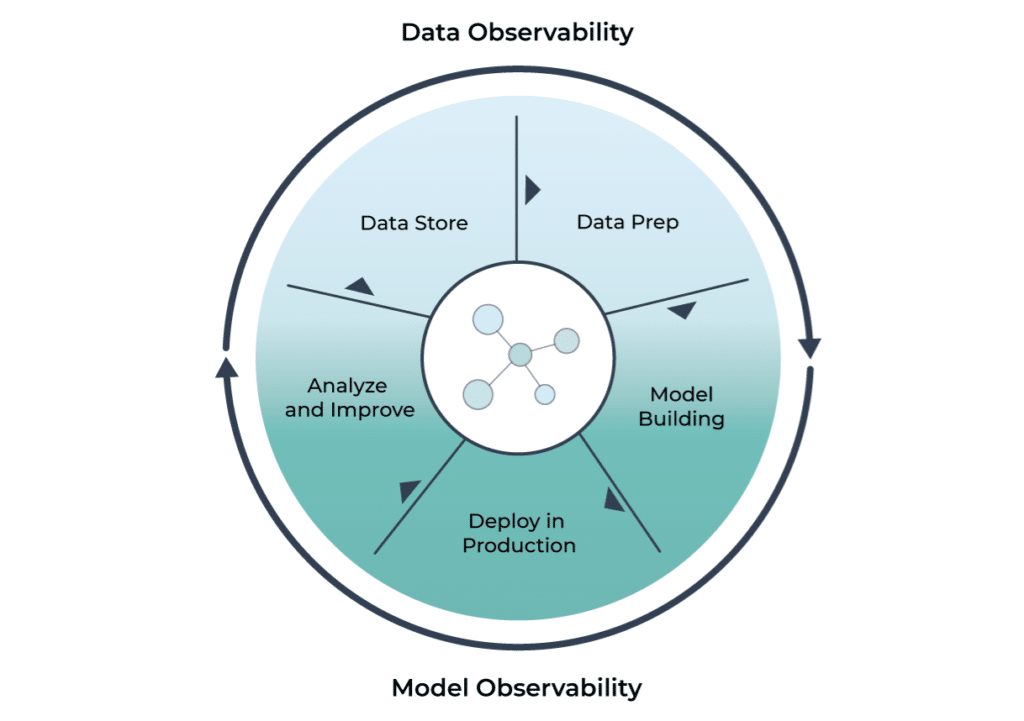
Implementing AI Observability
Implementing AI observability requires a combination of technical and organizational practices. On the technical side, data scientists and developers need to design ML models with observability in mind by:
- Incorporating logging
- Capturing metrics
- Monitoring capabilities.
Organizations also need to establish alerting mechanisms to notify them when issues arise and create dashboards to visualize the performance of ML models.
A few of the most prominent AI observability tools/platforms are Neptune.ai, Grafana + Prometheus, Whylabs, and Arize AI.
Free and Open-source Whylogs allow users to generate data profiles, which are statistical summaries of their data. These statistical summaries include crucial information about the data, such as its distribution, the number of missing values, the kind of data, etc. These profiles allow users to understand the data being put into their models, the predictions they are making, and the model’s performance. They can quickly discover problems like data drift, poor data quality, and more.

A lot of the MLOps recommended practises can be automated utilizing an AI observability platform in addition to this “human in the loop” observability. By automating these procedures, machine learning experts may concentrate on putting more models into use because they won’t have to spend as much time diagnosing and repairing problems with their already deployed ML systems.

Conclusion
AI observability is a critical practice for ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of ML models in production environments. By providing real-time visibility into ML operations, observability enables data scientists and developers to detect and diagnose issues quickly, assess the impact of changes, and optimize ML models’ performance. Implementing observability requires a combination of technical and organizational practices, and it is crucial for promoting transparency and accountability in the use of AI technologies. Observability is the key difference between a team that flies blind after deploying a model and a team that can iterate and improve its models quickly.